L'intelligence artificielle (IA) transforme la façon dont les entreprises de logistique réduisent les émissions et améliorent l'efficacité. Avec le transport responsable de 13 % des émissions mondiales de gaz à effet de serre, l'IA offre des solutions pour relever ces défis. Voici ce que vous devez savoir :
- Le rôle de l'IA : L'IA optimise les itinéraires de livraison, prédit les besoins en inventaire et automatise les opérations d'entrepôt, aidant à réduire les coûts logistiques de 15 % et les émissions jusqu'à 50 %.
- Outils clés : Les modèles prédictifs comme ARIMA et LSTM améliorent la précision des prévisions de la demande, tandis que l'apprentissage par renforcement ajuste les itinéraires en temps réel pour économiser le carburant et réduire le CO₂.
- Impact réel : Des entreprises comme SPAR Austria et Walmart ont considérablement réduit le gaspillage alimentaire et les émissions en utilisant des outils basés sur l'IA.
- Technologie autonome : Les véhicules autonomes et les robots d'entrepôt maximisent l'efficacité, répondant aux pénuries de main-d'œuvre et réduisant les temps d'arrêt opérationnels.
- Suivi des émissions : Les capteurs IoT combinés à l'IA permettent une surveillance en temps réel de la consommation de carburant et des émissions de carbone, garantissant la conformité aux réglementations strictes.
L'IA transforme la logistique avec des systèmes plus intelligents, des données en temps réel et des processus automatisés, ouvrant la voie à une chaîne d'approvisionnement plus verte.
Comment l'IA et les données révolutionnent les chaînes d'approvisionnement durables
Analyse prédictive alimentée par l'IA pour la demande et l'inventaire
La prévision basée sur l'IA est devenue un élément clé pour la logistique, aidant à réduire les déchets et les émissions dans les chaînes d'approvisionnement. Les méthodes traditionnelles sont souvent insuffisantes car elles reposent sur des hypothèses statiques, entraînant une surproduction et un excès d'inventaire. En revanche, les outils alimentés par l'IA comme ARIMA, XGBoost et les réseaux de mémoire à long court terme (LSTM) combinent les données historiques avec les entrées en temps réel - telles que la météo, le trafic et les tendances saisonnières - pour prédire les besoins en inventaire avec une bien plus grande précision. Cette prévision plus précise réduit les déchets et réduit considérablement les émissions de carbone [8].
L'IA brille également dans la gestion de l'incertitude. Les autoencodeurs variationnels (VAE), un type d'IA générative, simulent divers scénarios de demande, permettant aux entreprises de tester leur chaîne d'approvisionnement contre les perturbations ou les pics de demande [5]. En planifiant plusieurs résultats, les responsables logistiques peuvent construire des systèmes plus résilients tout en minimisant les déchets.
Et ce n'est pas tout - la précision de l'IA dans la prévision de la demande s'étend à l'optimisation de l'utilisation des ressources, réduisant davantage les inefficacités.
Réduire les déchets grâce à une meilleure prévision
Une meilleure prévision ne consiste pas seulement à améliorer l'efficacité ; il s'agit aussi de faire un impact environnemental significatif. Les systèmes d'IA peuvent réduire les émissions de CO2 par itinéraire de 30 % en alignant l'offre plus étroitement sur les modèles de demande [8]. Cet alignement minimise la surproduction, réduit la consommation d'énergie dans les entrepôts et garantit une utilisation plus efficace de la capacité de transport.
"Les projections précises de la demande sont essentielles pour prévenir les opérations logistiques liées au gaspillage." - VenkateshPrabu Parthasarathy, IJAIDSML [8]
Les données en temps réel collectées par les capteurs IoT - suivi de la consommation de carburant, de la vitesse du véhicule et des performances du moteur - permettent des ajustements dynamiques des itinéraires [8]. Cette boucle de rétroaction continue garantit que les entreprises peuvent réagir à des événements inattendus comme des changements météorologiques soudains, des embouteillages ou des pics de demande sans recourir à des plans de secours coûteux.
Les avantages pratiques de ces outils d'IA sont mieux visibles dans des exemples concrets.
Études de cas sur la gestion de l'inventaire basée sur l'IA
Prenez SPAR Austria, par exemple. En mars 2025, l'entreprise a adopté une solution de prévision de la demande basée sur l'IA utilisant Microsoft Azure. Le résultat ? Une précision de prévision supérieure à 90 %, ce qui a entraîné une réduction des coûts de 15 % en réduisant le gaspillage alimentaire [10]. Moins de produits expirés signifiait moins d'inventaire se dirigeant vers les décharges, marquant une étape importante vers la durabilité.
Un autre exemple provient de l'ensemble de données M5 Forecasting de Walmart, où les chercheurs ont utilisé un autoencodeur variationnel pour générer des scénarios de demande. Ces scénarios ont alimenté un algorithme génétique de tri non dominé (NSGA-II), qui a identifié des stratégies d'approvisionnement pouvant réduire les émissions de 50 % avec seulement une augmentation des coûts de 10-15 %. De plus, un agent Deep Q-Learning a amélioré les résultats de 10 % en optimisant les modes de transport [5].
Plus près de chez nous, une installation automobile à Blaj, en Roumanie, a mis en œuvre l'IA dans ses processus de réception d'entrepôt. Les résultats ont été frappants : une réduction de 79 % du temps de réception et des économies substantielles, grâce à une meilleure précision des données et à moins d'erreurs logistiques [9].
Ces exemples montrent comment l'IA transforme la gestion de l'inventaire, la rendant plus intelligente, plus verte et plus efficace.
Optimisation dynamique des itinéraires et sélection du mode de transport
L'optimisation des itinéraires alimentée par l'IA va bien au-delà de la simple recherche du chemin le plus court. En tenant compte des conditions en temps réel, elle réduit à la fois la consommation de carburant et les émissions. Contrairement aux systèmes traditionnels qui dépendent d'horaires fixes et de cartes statiques, les algorithmes d'IA analysent les données en direct des API de trafic, des mises à jour météorologiques et des capteurs IoT sur les véhicules. Cette rétroaction constante aide les systèmes logistiques à éviter les embouteillages, à réduire les temps d'inactivité et à éviter les détours inutiles. Le résultat ? Une consommation de carburant plus faible et moins d'émissions, grâce à l'adaptabilité de l'apprentissage par renforcement.
L'apprentissage par renforcement (RL) joue un rôle crucial ici. Les agents RL apprennent de leur environnement et ajustent les itinéraires de manière dynamique à mesure que les conditions changent - qu'il s'agisse d'un embouteillage soudain, d'une météo inattendue ou d'un changement de livraison de dernière minute. Par exemple, le routage basé sur RL a permis d'économiser 22 % de carburant tout en réduisant les émissions de CO₂ de 30 % [8]. De plus, ces systèmes résolvent le problème des "kilomètres à vide", où les camions aux États-Unis fonctionnent sans cargaison environ 30 % du temps. En optimisant les itinéraires, l'IA peut réduire ces kilomètres à vide à seulement 10-15 % [6].
L'IA ne s'arrête pas à la planification des itinéraires - elle aide également à déterminer la meilleure façon de transporter les marchandises. Des outils comme NSGA-II permettent aux planificateurs logistiques d'équilibrer des objectifs concurrents, tels que la réduction des coûts tout en améliorant la durabilité. La recherche utilisant l'ensemble de données M5 Forecasting de Walmart a révélé que ces méthodes pourraient réduire les émissions jusqu'à 50 % avec seulement une augmentation des coûts de 10-15 % [5]. De plus, les agents Deep Q-Learning peuvent basculer entre les modes de transport verts et conventionnels en temps réel, en fonction de facteurs tels que la tarification du carbone et les changements de demande, réalisant une réduction supplémentaire de 10 % des émissions [5].
Ajustements d'itinéraires en temps réel basés sur l'IA
Les données en temps réel des capteurs IoT, combinées aux mises à jour du trafic et de la météo, permettent aux systèmes d'IA d'affiner continuellement les itinéraires de livraison. Ce recalibrage en temps réel garantit non seulement des livraisons plus rapides, mais aussi des émissions plus faibles. Contrairement aux méthodes logistiques traditionnelles, qui reposent sur des plans statiques, les systèmes d'IA s'adaptent à la volée.
Prenez Uber Freight comme exemple. Sous la direction du PDG Lior Ron, l'entreprise a utilisé l'apprentissage automatique pour révolutionner le routage des véhicules et résoudre le problème des kilomètres à vide. Leur algorithme a réduit les kilomètres à vide de 30 % à seulement 10-15 %, réduisant considérablement le gaspillage de carburant et les émissions [6].
"En examinant des centaines de paramètres différents, nous avons pu rendre [ce modèle] suffisamment précis pour introduire une place de marché qui est maintenant dépourvue de toute friction, de conjectures et d'allers-retours" [6].
Un autre exemple provient de Mile, une plateforme logistique qui a intégré un système d'exploitation basé sur l'IA avec SAP en 2025. Ce système a permis l'exécution des commandes le jour même et l'expédition prédictive. Les résultats ? 90 % des commandes à la demande livrées le même jour, une réduction de 85 % du temps de planification manuel et une augmentation de 25 % de l'utilisation des fourgonnettes [4]. Ces exemples montrent comment l'IA non seulement optimise les itinéraires, mais transforme également les opérations logistiques entières. La capacité à s'adapter en temps réel est un élément clé par rapport aux méthodes traditionnelles.
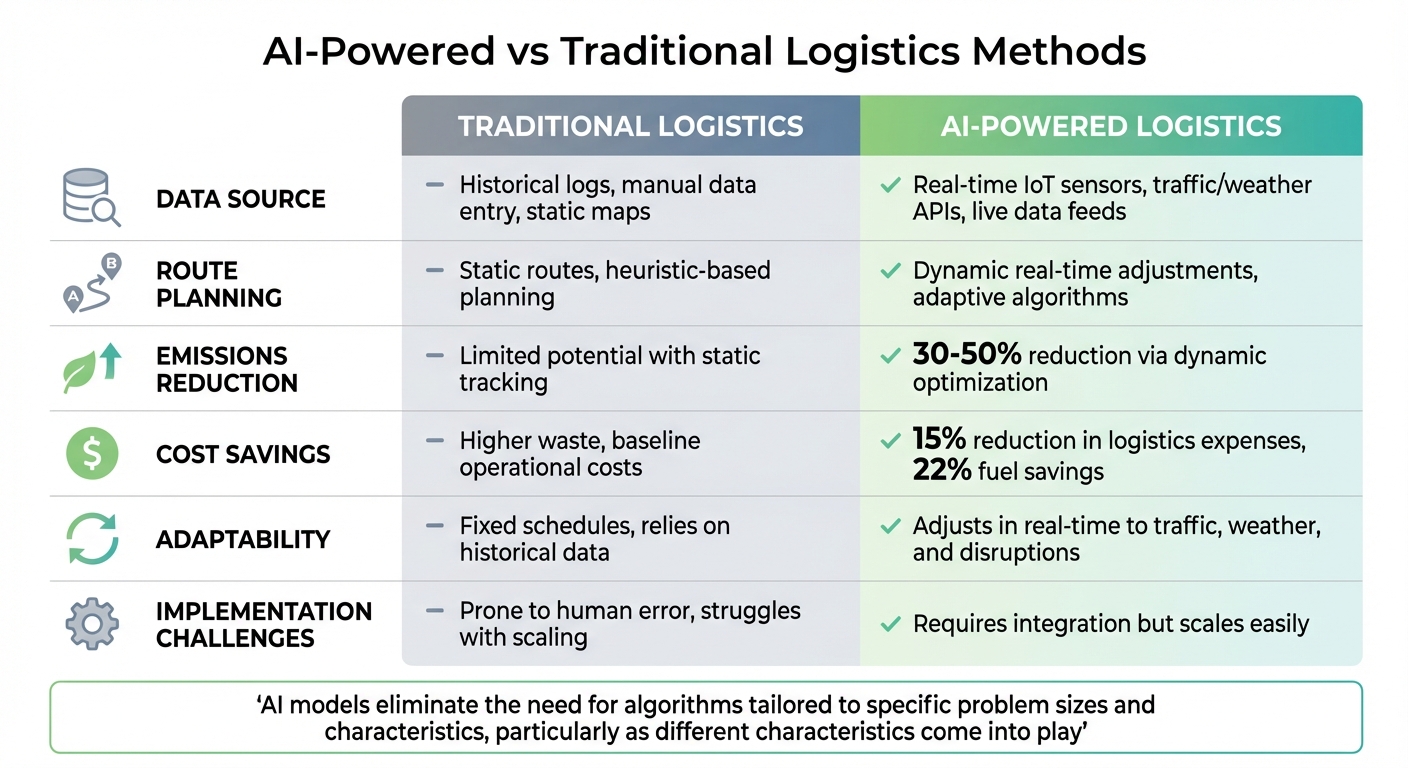
IA vs méthodes logistiques traditionnelles
Les différences entre la logistique basée sur l'IA et les méthodes traditionnelles sont frappantes, en particulier en ce qui concerne les émissions, les coûts et l'adaptabilité. Les systèmes traditionnels reposent sur des données historiques, des processus manuels et des cartes statiques - des approches sujettes aux erreurs et manquant de flexibilité. L'IA, en revanche, automatise la collecte de données et utilise des entrées en temps réel pour affiner continuellement les décisions.
| Caractéristique | Méthodes logistiques traditionnelles | Logistique alimentée par l'IA |
|---|---|---|
| Source de données | Journaux historiques, données manuelles, cartes statiques [8] | Capteurs IoT en temps réel, API de trafic/météo [8] [4] |
| Planification des itinéraires | Statique/heuristique [8] | Ajustements dynamiques en temps réel [8] [4] |
| Réduction des émissions | Potentiel limité avec suivi statique | Réduction de 30-50 % via optimisation dynamique [8] [5] |
| Économies de coûts | Déchets plus élevés, coûts de base | Réduction de 15 % des dépenses logistiques ; économies de carburant de 22 % [7] [8] |
| Adaptabilité | Repose sur des horaires fixes et des données historiques | S'ajuste en temps réel au trafic, à la météo et aux perturbations [8] |
| Défis de mise en œuvre | Sujette aux erreurs humaines ; difficultés à l'échelle | Nécessite une intégration mais se met à l'échelle facilement [8] |
"Les modèles d'IA éliminent le besoin d'algorithmes adaptés à des tailles et des caractéristiques de problèmes spécifiques, en particulier lorsque différentes caractéristiques entrent en jeu" [6].
Cette capacité à l'échelle rend les systèmes d'IA idéaux pour gérer des réseaux logistiques de plus en plus complexes sans ajustements manuels constants - un inconvénient clé des méthodes traditionnelles. En automatisant et en optimisant les processus, l'IA garantit que les opérations logistiques restent efficaces, même face à des défis en évolution.
sbb-itb-20a3bee
Véhicules autonomes et robotique en logistique
La capacité de l'IA à optimiser les itinéraires a déjà prouvé son efficacité dans la réduction des émissions, mais l'intégration des véhicules autonomes et de la robotique porte la logistique au niveau suivant. Ces technologies garantissent des opérations continues, réduisant la consommation de carburant et les émissions. Contrairement aux systèmes exploités par l'homme qui nécessitent des pauses et des changements d'équipe, les camions autonomes et les robots de livraison peuvent fonctionner 24 heures sur 24, ce qui entraîne des livraisons plus rapides et une plus grande efficacité. Cela intervient à un moment critique, car l'industrie du camionnage américaine a connu une pénurie d'environ 80 000 conducteurs en 2021 - un chiffre qui devrait doubler d'ici 2030. Ces avancées répondent non seulement aux lacunes de la main-d'œuvre, mais s'alignent également sur les objectifs environnementaux [12].
Véhicules de livraison autonomes et leur impact
Les véhicules de livraison autonomes combinent l'optimisation des itinéraires alimentée par l'IA avec des systèmes avancés de gestion des charges pour réaliser une logistique hautement efficace. En calculant les itinéraires les plus économes en carburant et en maximisant l'espace des camions ou des navires, ces systèmes minimisent les kilomètres gaspillés et réduisent le nombre de trajets nécessaires [10] [11] [14].
Un exemple pratique provient de Lisbonne, au Portugal, où une entreprise de logistique a introduit le cadre ECO.Logística en avril 2025. Cette initiative a combiné les véhicules électriques avec des outils d'optimisation basés sur l'IA, produisant des résultats impressionnants : une réduction de 15-20 % des délais de livraison, une amélioration de 10-25 % de l'efficacité énergétique et une diminution de 40 % des émissions de CO₂ [18].
Le rôle de l'IA ne s'arrête pas à la planification des itinéraires. Les systèmes de maintenance prédictive surveillent la santé des véhicules et les comportements de conduite en temps réel, garantissant que les moteurs fonctionnent efficacement et évitant les pannes qui gaspillent les ressources. Avec le transport routier représentant 53,8 % de tout le transport de fret dans les 27 pays de l'UE, ces mesures sont cruciales pour réduire les émissions [11].
Robotique alimentée par l'IA dans les entrepôts
Dans les entrepôts, la robotique alimentée par l'IA - telle que les robots mobiles autonomes (AMR) et les véhicules à guidage automatisé (AGV) - travaillent sans relâche, répondant à la demande fluctuante sans avoir besoin de personnel supplémentaire [12]. Ces robots améliorent l'utilisation de l'espace d'entrepôt jusqu'à 30 % grâce à des opérations précises et efficaces [19].
L'IA amplifie également la productivité humaine. Par exemple, un opérateur peut maintenant gérer une flotte de cinq à dix robots autonomes, un saut significatif par rapport au ratio traditionnel un-à-un. Josip Cesic, PDG de Gideon, souligne ce changement :
"Historiquement, un opérateur de chariot élévateur gérait un véhicule. Aujourd'hui, une personne peut exploiter une flotte de cinq à dix robots autonomes. C'est un gain d'efficacité significatif rendu possible par l'IA." [15]
Cette évolution non seulement augmente la productivité, mais améliore également la sécurité dans les environnements d'entrepôt occupés en réduisant les erreurs humaines. De plus, les délais d'exécution peuvent être réduits jusqu'à 25 % [12] [13] [19]. Ces avancées résolvent les pénuries de main-d'œuvre tout en promouvant la durabilité en optimisant la consommation d'énergie et en améliorant l'efficacité des ressources [11] [16].
Suivi des émissions en temps réel et gestion des risques
L'IA transforme la façon dont les émissions sont suivies et gérées, portant l'optimisation logistique au niveau suivant. En intégrant des capteurs IoT dans les camions et l'équipement, les plateformes d'IA collectent des données en direct sur la consommation de carburant, les performances du moteur, la vitesse et la consommation d'électricité. Cela remplace les rapports périodiques obsolètes par des mises à jour continues et en temps réel [8]. Les données circulent dans des systèmes centralisés, où l'IA les traite instantanément, formant l'épine dorsale des stratégies visant à réduire les émissions.
Le secteur de la logistique est un contributeur majeur aux émissions mondiales, représentant environ 14 % des gaz à effet de serre, le transport routier de fret seul étant responsable de plus de 60 % de ce chiffre [8]. L'IA résout ce problème en automatisant les calculs des émissions en utilisant la formule : Émissions de CO₂ = Carburant consommé × Facteur d'émission [8]. Les algorithmes d'apprentissage automatique (ML) et d'apprentissage par renforcement (RL) analysent à la fois les données historiques et en temps réel, permettant des prédictions précises des émissions et même un reroutage en temps réel pour réduire l'impact environnemental [8].
Outils d'IA pour l'analyse de l'empreinte carbone
Les outils d'IA fournissent maintenant des informations complètes dans les chaînes d'approvisionnement, suivi des émissions des véhicules individuels aux réseaux de fournisseurs entiers. Ces plateformes permettent aux entreprises de surveiller les émissions du Scope 3 - les émissions indirectes des fournisseurs et des partenaires - en analysant les dossiers d'approvisionnement et en vérifiant les affirmations environnementales avec des outils comme l'imagerie satellite [1]. Ce niveau de transparence est particulièrement critique pour respecter les réglementations strictes, telles que les directives ESG de l'Europe, qui exigent des rapports détaillés sur les émissions [1][20].
"L'IA est essentielle dans toute future boîte à outils environnementale. Elle peut révolutionner les efforts de durabilité, favorisant l'efficacité et la responsabilité au sein des chaînes d'approvisionnement."
Au-delà du suivi des émissions, l'IA joue maintenant un rôle vital dans l'identification et la gestion des risques opérationnels.
Identification des risques par l'IA
L'IA excelle à repérer les risques avant qu'ils ne perturbent les opérations. Les méthodes traditionnelles - comme les journaux manuels et les feuilles de calcul - sont souvent trop lentes pour détecter des problèmes tels que les retards d'approvisionnement, les perturbations météorologiques ou les goulots d'étranglement du transport [8]. L'IA, en revanche, analyse des sources de données non conventionnelles comme les dossiers judiciaires, l'analyse des sentiments et l'imagerie satellite pour découvrir des risques cachés, y compris les pratiques contraires à l'éthique des fournisseurs ou les violations réglementaires [1].
Lorsque des perturbations se produisent, les systèmes d'IA peuvent recommander ou même mettre en œuvre des solutions en temps réel. Par exemple, Dow Chemical utilise un agent de facturation alimenté par l'IA construit avec Microsoft Copilot Studio pour gérer 4 000 expéditions quotidiennes. Ce système analyse les e-mails, organise les données et identifie les erreurs de facturation, réduisant les surpaiements et améliorant l'efficacité des coûts [10]. Notamment, 70 % des entreprises utilisant l'IA pour l'approvisionnement éthique rapportent qu'elle identifie les risques qu'elles auraient autrement manqués [1].
L'IA soutient également la planification d'urgence grâce à des outils comme les jumeaux numériques, alimentés par l'IA générative. Ces simulations permettent aux responsables de modéliser des scénarios "et si", tels que des fermetures d'usines simultanées ou des pénuries de matériaux, leur permettant de préparer des stratégies qui maintiennent l'efficacité opérationnelle tout en maîtrisant les émissions [21].
Points clés et perspectives d'avenir
Résumé des tendances clés
L'IA transforme la logistique par plusieurs avancées révolutionnaires. L'analyse prédictive, alimentée par des modèles comme LSTM et XGBoost, affiche maintenant une précision de prévision supérieure à 90 %. Par exemple, SPAR Austria a réussi à réduire les coûts de 15 % dans 1 500 magasins en réduisant le gaspillage alimentaire grâce à la prévision de la demande basée sur l'IA en mars 2025 [10]. De même, les algorithmes d'apprentissage par renforcement ont réalisé des économies de carburant de 22 % en s'adaptant aux conditions de trafic et de météo en temps réel, surpassant les méthodes de routage traditionnelles [8]. Les systèmes autonomes sont également en hausse - Amazon a rapporté le déploiement de plus de 200 000 robots alimentés par l'IA dans ses entrepôts en novembre 2025 [4]. Pendant ce temps, l'intégration IoT en temps réel permet une surveillance continue des émissions, aidant les entreprises à réduire la production de CO₂ jusqu'à 30 % par itinéraire [8].
Un changement significatif se produit, passant de l'automatisation de base à l'"IA agentique" - des systèmes qui observent, planifient et exécutent activement les tâches. Les modèles de raisonnement avancés ont démontré leur potentiel en réduisant les coûts de la chaîne d'approvisionnement de 67 % dans les simulations par rapport aux équipes dirigées par l'homme [17]. Malgré cela, seulement 10 % des entreprises de logistique ont pleinement adopté l'IA générative, même si plus d'un tiers des cadres reconnaissent son potentiel transformateur [3].
L'avenir de l'IA en logistique
En regardant vers l'avenir, le rôle de l'IA en logistique devrait s'étendre encore davantage. S'appuyant sur les avancées actuelles comme l'analyse prédictive, le routage dynamique et les systèmes autonomes, l'impact économique de l'IA en logistique devrait atteindre entre 1,3 trillion et 2 billions de dollars par an au cours des deux prochaines décennies [10]. Les modèles de raisonnement avancés, qui reposent sur des boucles plan-exécution-réflexion plutôt que sur une simple reconnaissance de motifs, devraient devenir la norme, réduisant les coûts de 70 % par rapport aux technologies d'IA antérieures [17]. L'intégration de l'IA avec les flottes de véhicules électriques optimisera également les calendriers de recharge et la gestion de l'autonomie, accélérant le passage aux transports à zéro émission [8][2].
Cependant, des défis demeurent. La mauvaise qualité des données est un obstacle important, 48 % des entreprises l'identifiant comme leur plus grand obstacle. De plus, les demandes énergétiques des systèmes d'IA ne sont souvent pas comptabilisées dans les métriques ESG, et les problèmes de confiance persistent - environ 50 % des cadres expriment des préoccupations concernant l'équité des décisions basées sur l'IA [1]. Comme le Boston Consulting Group l'a souligné, "l'adoption proactive [de GenAI] n'est plus facultative mais impérative" [3].
FAQ
Comment l'IA améliore-t-elle la prévision de la demande dans la logistique durable ?
L'IA transforme la prévision de la demande dans la logistique durable en traitant les données en temps réel provenant de diverses sources, y compris les tendances des médias sociaux, les mises à jour météorologiques et les signaux économiques. Utilisant des techniques avancées d'apprentissage automatique telles que l'apprentissage par renforcement et l'apprentissage fédéré, elle fournit des prédictions précises et adaptables.
Ces prévisions améliorées minimisent les erreurs d'inventaire, rationalisent les processus de la chaîne d'approvisionnement et améliorent l'adaptabilité aux besoins du marché changeants. Le résultat ? Une approche plus efficace et respectueuse de l'environnement de la logistique.
Comment les véhicules autonomes aident-ils à réduire les émissions en logistique ?
Les véhicules autonomes transforment la logistique en réduisant les émissions grâce à l'optimisation des itinéraires alimentée par l'IA et à la technologie autonome. Ces outils sont conçus pour minimiser la consommation de carburant, rendant le transport longue distance plus efficace et respectueux de l'environnement.
En éliminant les kilomètres inutiles et en rationalisant les opérations, ces véhicules réduisent non seulement les coûts opérationnels, mais soutiennent également les pratiques logistiques plus vertes. Ce changement aide les entreprises à atteindre leurs objectifs environnementaux tout en améliorant l'efficacité globale.
Comment l'IA aide-t-elle les entreprises de logistique à respecter les réglementations environnementales ?
L'IA transforme la façon dont les entreprises de logistique gèrent la conformité aux réglementations environnementales en décomposant les règles complexes en étapes claires et exploitables. Par exemple, les outils alimentés par l'IA peuvent surveiller les émissions de carbone en temps réel des camions, des entrepôts et des opérations de fret, présentant ces données en termes mesurables comme les livres ou les tonnes métriques. Ces plateformes peuvent également automatiser la génération de rapports pour les agences de réglementation, signaler les expéditions qui dépassent les limites d'émission et recommander des options plus vertes, telles que les itinéraires optimisés ou le passage aux véhicules électriques.
En plus de la conformité, l'IA améliore l'efficacité opérationnelle pour réduire les émissions. Les algorithmes avancés aident à réduire les temps d'inactivité, à réduire la consommation de carburant et à assurer le respect des normes d'efficacité énergétique comme les exigences américaines Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE). L'analyse prédictive peut même anticiper les ajustements de flotte, permettant aux entreprises de rester en avance sur les mandats d'émissions zéro et d'éviter les pénalités coûteuses.
L'IA simplifie également la conformité administrative en extrayant automatiquement les données clés des factures et des dossiers, économisant du temps et réduisant les erreurs. En consolidant tous les informations dans un seul tableau de bord convivial, les responsables logistiques peuvent facilement suivre les progrès, respecter les attentes réglementaires et même utiliser la conformité comme avantage concurrentiel dans leurs opérations.