By 2050, 66% of the global population - over 2.5 billion people - will live in cities. This rapid urbanization is driving demand for AI experts to solve challenges in transportation, energy, and public safety. AI-powered solutions are transforming urban life while creating high-paying jobs in fields like data science, transportation systems, and infrastructure analysis.
Here’s what you need to know:
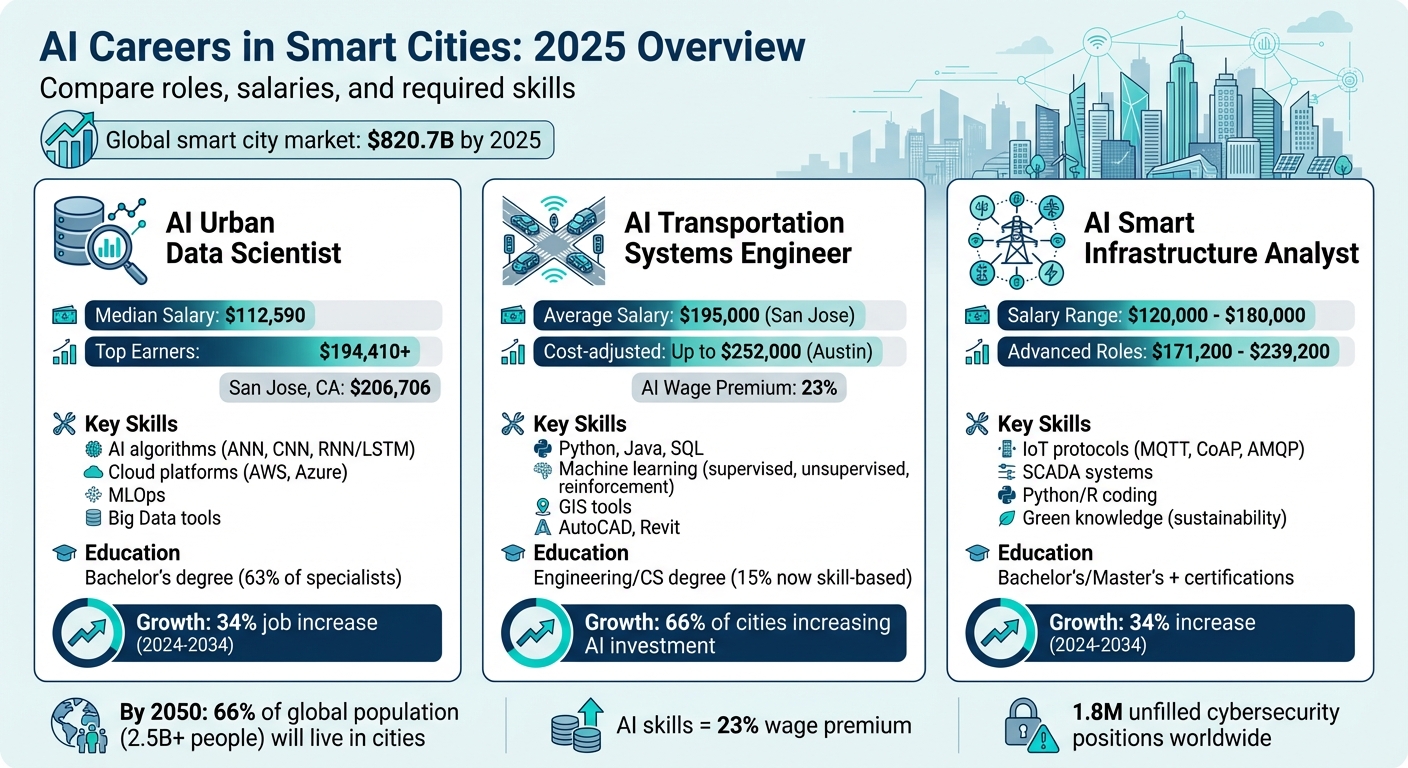
- AI Urban Data Scientists analyze data from IoT devices to improve traffic, air quality, and city planning. Median salary: $112,590 (2024). Skills: AI algorithms, cloud platforms, and MLOps.
- AI Transportation Systems Engineers design smart traffic systems and digital twins for real-time urban management. Average salary: $195,000 in San Jose, CA. Skills: Python, machine learning, and GIS tools.
- AI Smart Infrastructure Analysts integrate AI into power grids, water systems, and street lighting. Salaries range from $120,000 to $180,000. Skills: IoT protocols, SCADA systems, and coding.
The global smart city market is projected to reach $820.7 billion by 2025. AI expertise offers a 23% wage premium, and skill-based hiring is growing, making certifications and hands-on experience more valuable than degrees. Tools like Acedit provide affordable, targeted preparation for these roles, helping candidates improve technical and interview skills.
Urban AI careers combine technical knowledge with urban planning and sustainability insights. With 34% growth expected in data science jobs by 2034, now is the time to build the skills needed for this fast-evolving field.
AI Smart City Careers: Roles, Salaries, and Skills Comparison 2025
1. AI Urban Data Scientist
Responsibilities
AI Urban Data Scientists play a key role in transforming data from over 1.6 billion IoT devices into actionable insights to address urban challenges. These devices include traffic sensors, weather stations, and energy monitors, all of which generate data that these professionals analyze to help improve city life. Their work involves building machine learning models, ensuring ethical AI practices, and presenting their findings in clear, visual formats for city planners and the public. Tasks range from uncovering the causes of traffic gridlocks to calculating the required size of city sewer pipes. They also develop systems for traffic optimization, smart routing, and monitoring environmental factors like air quality and flood risks. This role demands both technical expertise and strong communication skills.
Required Skills
To succeed in this field, AI Urban Data Scientists need a mix of technical and interpersonal abilities. Proficiency in AI algorithms like ANN, CNN, and RNN/LSTM is a must. Familiarity with Big Data tools, cloud platforms like AWS and Azure, and statistical modeling is equally important. They must also understand IoT infrastructure and be skilled in MLOps to manage AI projects from start to finish. Beyond technical skills, they need to communicate complex findings effectively to non-technical audiences, think creatively about urban issues, and take responsibility for how their models influence city policies. A background in urban planning, environmental practices, and security standards further strengthens their profile.
Education Requirements
Most roles require at least a bachelor's degree in AI, Machine Learning, Data Science, or a related technical field. While 63% of AI specialists hold a bachelor’s degree, about 17% have pursued advanced education, such as a master’s degree. For those transitioning into the field, online courses can help build the necessary skills.
Salary Ranges
AI Urban Data Scientists are well-compensated for their expertise. As of May 2024, the median annual wage for data scientists was $112,590, with top earners making over $194,410. Positions requiring AI skills generally pay about 25% more than similar roles without those skills. Salaries also vary by location - data scientists in San Jose, CA, average $206,706 annually, compared to $146,650 in Seattle, WA. In December 2025, Amazon Web Services advertised data scientist roles for its US Federal division in Herndon and Arlington, VA, offering salaries between $125,500 and $212,800 per year. Experience significantly influences pay; professionals with 10–14 years of experience earn a median salary of $172,361, while those just starting (0–1 years) earn $103,015.
Growth Opportunities
The demand for AI Urban Data Scientists is growing rapidly. Employment in data science is expected to increase by 34% from 2024 to 2034, far outpacing the average growth rate across all occupations. Additionally, the global smart city market is projected to reach $820.7 billion by 2025, further fueling demand for this role. Advanced positions, such as Director or VP of AI/Machine Learning, offer significant salary growth. Some professionals branch out into specialized roles, such as Experiential Officers, who focus on resident satisfaction, or Smart Infrastructure Analysts, who manage the integration of physical and digital city systems. These career paths highlight the pivotal role this position plays in shaping the future of urban living.
"This career is the sexiest job of the 21st century. And, why not? After all, smart cities exist because of data." - William Goddard, Founder, IT Chronicles
2. AI Transportation Systems Engineer
Responsibilities
AI Transportation Systems Engineers are at the forefront of designing smart traffic systems. Their work involves creating systems that adapt to real-time conditions, reducing congestion and predicting infrastructure issues by analyzing sensor data. A key tool in their arsenal is the development of digital twins - virtual replicas of city infrastructure. These models simulate scenarios like traffic flow, emergency responses, and the long-term effects of urban planning decisions. A notable example of this is San Zuniga's work in Miramar, FL, in November 2025, where digital twins played a crucial role in optimizing city operations. These engineers also integrate data from IoT sensors, traffic cameras, and third-party mobility services into a unified system, giving city planners instant insights and better control over urban environments. The role is both technically demanding and analytically intensive, requiring a diverse skill set to manage these dynamic challenges.
Required Skills
To succeed in this role, engineers need a solid foundation in engineering principles, advanced AI expertise, and strong programming skills in languages like Python, Java, and SQL for handling massive urban datasets. They must also be skilled in machine learning techniques. For instance, supervised learning can detect structural issues like bridge cracks, unsupervised learning can identify patterns in transit usage, and reinforcement learning can optimize city-wide traffic signals. A real-world example comes from the Texas Department of Transportation, which tested reinforcement learning algorithms in September 2023. These algorithms dynamically adjusted signal timing during incidents, outperforming traditional pre-timed systems. Beyond technical know-how, engineers need excellent analytical skills and the ability to communicate complex AI findings in ways that city planners and stakeholders can act on. Familiarity with tools like AutoCAD, Revit, and GIS mapping software is also highly beneficial.
Education Requirements
While many positions require a bachelor’s degree in engineering, computer science, or urban planning, the industry is gradually shifting toward skill-based hiring. About 15% of employers now prioritize hands-on experience and certifications over formal education. Many professionals enhance their qualifications through bootcamps, online courses, and micro-credentials, making the field more accessible to a broader range of candidates.
Salary Ranges
Salaries for AI Transportation Systems Engineers are competitive and vary by region. For example, in San Jose, CA, average salaries hover around $195,000. However, adjusting for cost of living, midpoints in cities like Austin, TX, can reach $252,000. Other cities, such as Jacksonville, FL, and Houston, TX, show similar trends, with a 23% wage premium attributed to AI expertise.
Growth Opportunities
The future looks bright for this field, with 66% of 167 surveyed cities planning to increase their AI investments, and 80% aiming to boost spending by 2027. The demand for AI fluency - the ability to effectively use and manage AI tools - has surged sevenfold in just two years. By 2030, AI-powered systems and robots are expected to generate nearly $2.9 trillion in economic value in the United States. Career growth in this field isn’t limited to engineering. Professionals can branch into areas like AI Governance and AI Auditing, ensuring transportation models are fair and unbiased. Others focus on climate resilience, using environmental data to make transit networks more robust against extreme weather. For instance, the City of Cascais in Portugal implemented a digital platform between 2019 and 2024 that optimized waste collection routes in real time. This initiative saved 180,000 kilometers of travel, reduced CO₂ emissions by 350 tons, and cut annual costs by approximately €600,000.
"Work in the future will be a partnership between people, agents, and robots - all powered by AI." - McKinsey
3. AI Smart Infrastructure Analyst
Responsibilities
AI Smart Infrastructure Analysts play a critical role in weaving AI technologies and IoT sensors into essential city systems like power grids, water networks, and street lighting. A major focus of their work is energy management - developing smart metering systems, refining power distribution, and implementing renewable energy solutions such as solar microgrids. For example, in December 2025, Austin, Texas showcased the potential of smart grids when analysts integrated solar microgrids with battery storage and real-time consumption monitoring. This effort enabled automated load balancing and predictive maintenance. These professionals also design systems for real-time monitoring and automated responses to manage city assets more efficiently, all while ensuring compliance with regional energy policies and grid standards.
Required Skills
To meet these demands, AI Smart Infrastructure Analysts need a robust set of technical skills. They must be adept in IoT protocols like MQTT, CoAP, and AMQP, as well as cloud platforms such as AWS IoT Core and Azure IoT Hub. Familiarity with SCADA systems, Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), and grid modernization technologies is crucial. Additionally, coding skills in Python or R and experience with design tools like AutoCAD or Revit are essential. Beyond technical expertise, these roles require strong critical thinking, ethical decision-making, and the ability to simplify complex infrastructure concepts for stakeholders. Another unique aspect of this role is the need for "Green knowledge", which includes urban environmental design, water management, and circular economy principles.
Education Requirements
Most positions require at least a bachelor’s or master’s degree in fields like computer science, data science, or engineering. However, there’s a growing trend toward skill-based hiring, where hands-on certifications are valued alongside formal education. Advanced roles often benefit from interdisciplinary backgrounds that combine engineering with social sciences or public policy. Certifications such as the Certified Information Privacy Professional (CIPP) or specialized training programs from DeepLearning.ai and Microsoft can further enhance a candidate’s qualifications.
Salary Ranges
AI Smart Infrastructure Analysts are well-compensated for their expertise. AI engineers typically earn between $120,000 and $180,000 annually, while data engineers see salaries ranging from $110,000 to $155,000. Professionals advancing to roles like AI Cloud Architect or Platform Lead can command median salaries of $171,200, with top earners reaching up to $239,200. The demand for AI skills often results in a wage premium, reflected in the higher salaries for advanced positions.
Growth Opportunities
The career outlook for this field is incredibly promising. Job growth in data science roles related to infrastructure analysis is expected to rise by 34% between 2024 and 2034. Professionals can advance from hands-on technical roles to system-level positions like AI Cloud Architect or pivot into strategic leadership roles such as AI Product Manager or Solutions Architect. Specialists might also focus on areas like MLOps to ensure scalable AI reliability or AI Governance to maintain compliance with urban regulations. With the global smart city market projected to hit $820.7 billion by 2025, opportunities abound for those skilled in integrating systems like grid-connected buildings and smart EV charging networks. These advancements not only strengthen urban infrastructure but also pave the way for continuous career growth in smart city development.
How AI is Revolutionizing Municipal Engineering & Smart City Infrastructure
sbb-itb-20a3bee
4. Acedit (as a career preparation tool)
Acedit is designed to help candidates navigate the unique challenges of smart city AI interviews, combining technical expertise with ethical considerations. Breaking into this field requires not just knowledge but also the ability to perform well in complex interview scenarios. Acedit, an AI-powered Chrome extension, supports job seekers by offering real-time interview coaching, personalized Q&A generation, and AI-driven simulations tailored specifically for urban tech roles. It connects the dots between technical skills and effective interview performance, ensuring you're well-prepared for these demanding positions.
One standout feature is Acedit's LinkedIn integration, which aligns your preparation with the specific requirements of urban tech roles and company expectations. The tool generates practice questions that mirror the technical depth and ethical challenges you’re likely to encounter, including critical topics like privacy - a concern for 88% of citizens - and cybersecurity, an area with 1.8 million unfilled positions worldwide.
For those transitioning from traditional roles into smart city careers, Acedit provides a clear path for re-skilling, addressing the growing demand for specialized skills in this sector. William Goddard, Founder of IT Chronicles, highlights this need:
"Technological progress creates demand for new skillsets and renders old skill sets obsolete... People at risk can protect themselves from redundancy by retraining".
Acedit's AI simulation feature builds confidence by mimicking technical interview scenarios, while its real-time coaching offers immediate feedback on both technical precision and communication style. This dual approach helps candidates refine their performance and stand out in the hiring process.
To accommodate various preparation needs, Acedit offers flexible pricing plans:
- Free: Includes basic practice Q&As.
- Premium: $45 one-time fee for unlimited Q&As and six simulations.
- Premium Plus: $75 for unlimited access to all features.
With the global smart city market projected to hit $820.7 billion by 2025, investing in targeted interview preparation through tools like Acedit can significantly boost your chances of securing a role in this rapidly growing industry.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Pursuing a career in AI within smart cities comes with its own set of challenges and rewards. The table below outlines how different roles - and tools like Acedit - compare across three key aspects: skill development, career growth potential, and accessibility.
| Role / Tool | Skill Development | Career Advancement Potential | Ease of Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Data Scientist | High; requires expertise in database modeling, SQL, and big data processing. | Very High; demand for AI roles grew 21% between 2018 and 2023. | Moderate; a broad computer science background is essential. |
| Transportation Systems Engineer | High; involves real-time traffic data, machine learning, and optimization. | High; vital for sustainable cities and tied to a global market exceeding $800 billion. | Low; typically demands an engineering degree and over 10 years of experience. |
| Smart Infrastructure Analyst | High; focuses on environmental data and disaster risk management. | High; crucial for planning climate-resilient cities. | Moderate; requires navigating fragmented city strategies, which affect 90% of urban areas. |
| Acedit (Career Tool) | High; emphasizes in-demand AI skills like Python and machine learning. | High; aligns with the 23% wage premium associated with AI skills. | High; supports skill-based hiring trends over formal degrees. |
This table highlights the strengths and limitations of each role. Below, we dive deeper into the opportunities and challenges they present.
AI expertise offers a compelling 23% wage premium, outstripping most university degrees except PhDs, which yield a 33% premium. Interestingly, the emphasis on formal degrees for AI roles has dropped by 15%, as employers increasingly value proven skills over traditional qualifications. According to Mike Chmura of Chmura Economics & Analytics, “87% of executives report difficulty finding candidates with the right skillsets”. This shift creates openings for individuals who can demonstrate their abilities through alternative credentials like bootcamps or micro-certifications.
Urban Data Scientists are experiencing rapid growth, with a projected 34% increase in demand from 2024 to 2034. However, they face hurdles like managing inconsistent datasets and addressing privacy concerns, which affect 88% of citizens. Transportation Systems Engineers, while critical to sustainable urban development, often need a decade or more of specialized experience. Meanwhile, Smart Infrastructure Analysts contend with fragmented city planning processes - 90% of urban areas lack integrated strategies.
For those looking to break into these fields, Acedit offers a practical solution. With unlimited practice Q&As and simulations, its $75 Premium Plus plan provides an affordable alternative to traditional graduate programs. By focusing on skill-based preparation, Acedit aligns with the growing preference for demonstrable abilities over formal education. This is particularly relevant for the 500,000+ workers in cities like New York who face automation risks.
Conclusion
The demand for AI careers in smart cities is surging, with the market projected to hit $820.7 billion by 2025. Roles like Urban Data Scientists, Transportation Systems Engineers, and Smart Infrastructure Analysts require a blend of technical AI expertise and knowledge of urban planning, privacy, and sustainability. As William Goddard aptly states, "A city cannot be termed 'smart' if the residents feel their needs remain unmet and their quality of life hasn't improved". This highlights the importance of pairing technical skills with an understanding of urban dynamics. These careers call for professionals who can merge technical know-how with strategic urban insights, making continuous learning and alternative credentials more essential than ever.
To thrive in this evolving field, professionals need to embrace skill-based hiring and ongoing upskilling. This shift moves beyond traditional degrees, focusing instead on real-world expertise. Tools like Acedit are leading the charge, combining technical preparation with real-time coaching to help candidates excel. Acedit's targeted interview coaching is a prime example of how professionals can prepare for the interdisciplinary challenges of these roles.
As smart city technologies continue to advance - from digital twins to autonomous vehicle networks - success will depend on mastering both technical depth and broader skills like stakeholder collaboration and empathy. The projected 27.9% growth in Data Science careers between 2016 and 2026 underscores the demand for this unique skill set. However, only those who balance technical expertise with the softer skills necessary for effective urban governance will stand out.
For those considering this path, focus on building practical skills over relying solely on traditional degrees. Certifications like the Certified Information Privacy Professional (CIPP) address real-world challenges and can be game-changers for career growth. Programs that incorporate work-integrated learning in urban environments are also invaluable. The time to develop the skills needed for AI-driven smart cities is now.
FAQs
What skills are essential for AI careers in smart cities?
Working in AI roles within smart cities demands a blend of technical know-how and interpersonal abilities. Let’s break it down.
On the technical side, having a solid grasp of machine learning, data analytics, and programming languages like Python or Java is essential. These skills are the backbone for processing data from IoT sensors, which power systems like traffic management or energy efficiency solutions. Knowledge of IoT integration, DevOps methodologies, and analytics tailored for smart cities can give you an edge.
But technical skills alone won’t cut it. Soft skills are equally critical. Problem-solving, analytical thinking, and creativity are key to navigating the ever-evolving AI landscape. And since smart city projects often involve cross-disciplinary teams, strong communication and collaboration skills are a must to bring innovative urban solutions to life.
Want to stand out? Tools like Acedit can help. This AI-powered Chrome extension offers real-time interview coaching, generates personalized Q&A, and even helps craft tailored cover letters. It’s a handy way to confidently showcase your skills and land a role in shaping the cities of tomorrow.
What role do AI Urban Data Scientists play in city planning?
AI Urban Data Scientists are key players in crafting smarter, more efficient cities by diving deep into massive datasets. These data sources include everything from sensor readings and mobility patterns to energy consumption and socioeconomic trends. By leveraging machine learning models, they can forecast shifts in traffic flow, housing markets, and neighborhood development. This allows urban planners to test scenarios - like introducing a new transit line or rezoning an area - before making expensive commitments.
Another powerful tool in their arsenal is the creation of digital twin simulations. These are real-time, virtual replicas of a city's physical and social systems. With these simulations, scientists can pinpoint optimal spots for EV charging stations, balance energy consumption across neighborhoods, or fine-tune waste collection routes to cut emissions and save money.
On top of all this, AI Urban Data Scientists play a crucial role in shaping policies that prioritize fairness and inclusivity. By examining data on social inclusion and housing affordability, they provide insights that help design strategies to enhance public safety, promote equity, and ensure cities remain livable and accessible for everyone.
Why are employers prioritizing skills over degrees for AI roles?
The fast-paced growth of AI technology is reshaping what employers value most in potential hires. Practical skills and hands-on experience are now taking center stage, often outweighing the importance of traditional degrees. Why? Because demonstrated technical abilities and real-world know-how are proving to be stronger indicators of a candidate's readiness to tackle the challenges AI roles present today.
This shift is also opening doors for a wider range of talent. Employers are increasingly considering candidates who have gained their expertise through non-traditional routes, such as certifications, coding bootcamps, or self-directed learning. By broadening their hiring criteria, companies can not only fill roles more quickly but also feel more confident in the ability of these candidates to hit the ground running and deliver results.