AI is reshaping industries, automating routine tasks while creating new opportunities. By 2030, up to 30% of work hours in the U.S. could be automated, impacting 12 million workers who may need to switch careers. Lower-wage roles like customer service and office support face the highest risks, while healthcare and skilled trades remain more secure due to their reliance on human expertise. Key trends include:
- Job Loss: 10.4 million U.S. jobs could be displaced by AI, with generative AI responsible for half.
- Job Creation: Globally, 170 million jobs are expected to emerge by 2030, leading to a net gain of 78 million positions.
- Tech Industry: Entry-level roles are declining as AI automates routine tasks, but demand for AI oversight roles is increasing.
- Customer Service/Admin: High automation risk, but hybrid roles combining AI and human oversight are growing.
- Healthcare/Trades: AI supports rather than replaces workers, emphasizing skills like empathy and physical dexterity.
To stay competitive, workers should focus on developing AI fluency and skills that complement automation while leveraging tools like Acedit to prepare for the evolving job landscape.
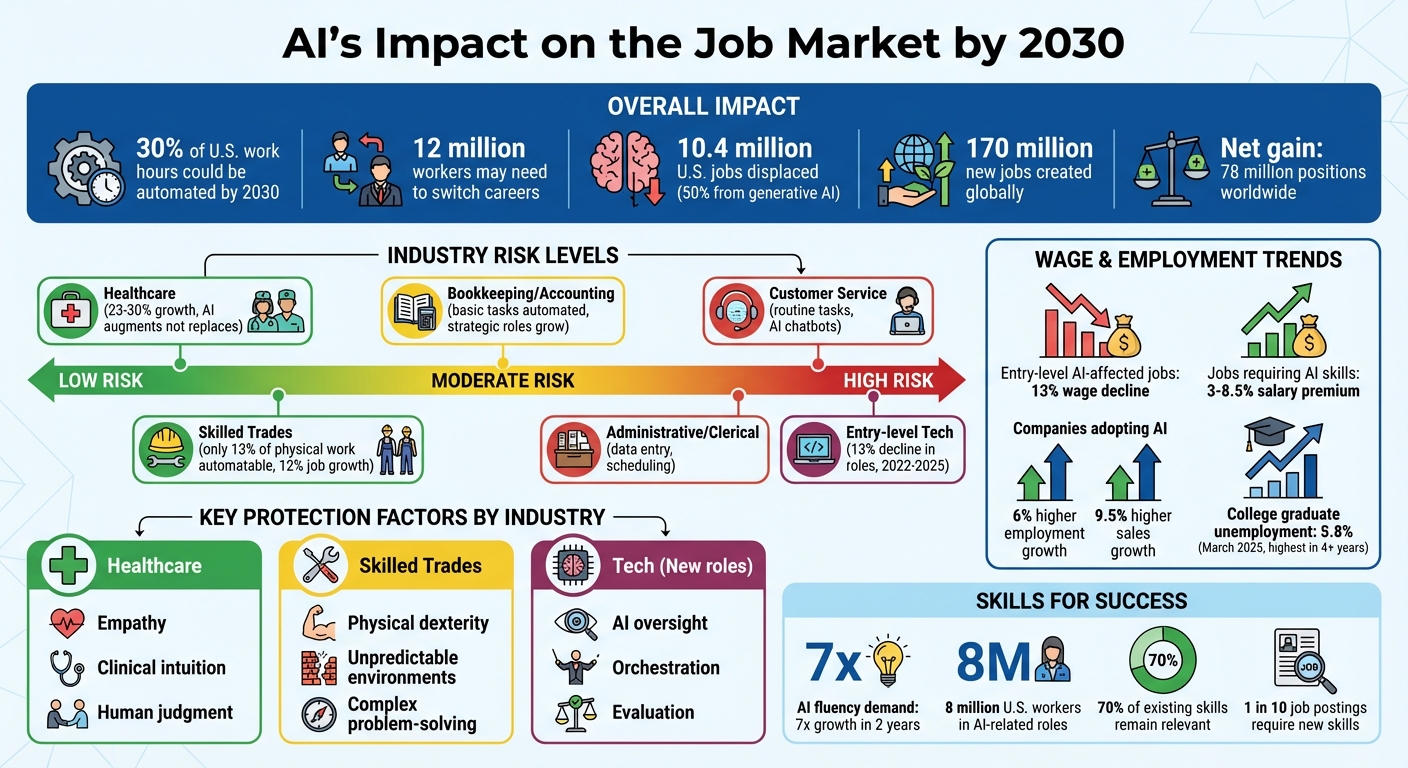
AI Job Market Impact by 2030: Displacement, Creation, and Industry Risk Levels
AI Job Loss Fears vs Reality: What 2025 Actually Showed | Firstpost Tech & Trade
Technology Sector: Automation and New Job Types
The tech industry is undergoing a major shift in how it approaches hiring and job roles. AI is not just changing what developers do - it’s also reshaping the qualifications and experiences that companies prioritize.
Changes in Entry-Level Coding and Software Development
Entry-level tech jobs are becoming less common. Between late 2022 and July 2025, roles for early-career workers in AI-affected tech positions dropped by 13%, with declines ranging from 6% to 16%. Meanwhile, jobs for experienced professionals grew by 6–9%.
Why is this happening? AI is automating routine tasks like code completion and bug fixes - tasks that used to help junior developers build their skills. Now, job-specific expertise and hands-on experience, which are harder to replace with automation, have become critical for staying relevant. But this raises a tough question: if entry-level tasks are automated, how will junior developers gain the skills they need?
"employment has begun to decline for young workers in highly exposed occupations like coding and call centers, but older workers and workers who use AI to augment, not automate work have seen job gains".
As these entry-level positions shrink, the industry is creating new roles that focus on managing and improving AI systems.
New Roles in AI Oversight and Management
To address the decline in traditional entry-level roles, the tech sector is seeing a surge in specialized jobs centered on AI oversight. The demand for AI-related skills has skyrocketed, with about 8 million workers in the U.S. now employed in roles requiring at least one AI-related competency.
New positions are emerging to meet these needs. For instance, professionals are taking on roles like AI Conductors, who manage AI tools and workflows rather than writing manual code. Other examples include Agent Product Managers, responsible for the lifecycle of autonomous agents, and AI Evaluation Writers, who create benchmarks to test AI performance. There’s even a developing field called "vibe engineering" (or context engineering), which focuses on optimizing how AI systems reason and make decisions.
"Software development is moving from 'people producing artifacts, assisted by tools' to 'teams orchestrating AI‑accelerated systems with human judgment at the core'".
This shift presents both challenges and opportunities. While automation reduces the need for routine programming, there's a growing demand for professionals who can oversee AI systems, craft precise prompts, enforce safeguards, and validate outputs. For newcomers to the field, the key is to develop skills in AI orchestration, oversight, and the kind of nuanced problem-solving that AI can't replicate.
Customer Service and Administrative Roles: High Automation Risk
Customer service and administrative jobs are among the most vulnerable to automation. Unlike the gradual integration of AI in tech-focused roles, these sectors face swift and direct disruption. The reason? Many tasks in these fields can be handled by AI with high accuracy - and at a much lower cost.
Automation in Call Centers and Bookkeeping
Customer service representatives top the list of jobs most at risk of automation. Their daily tasks - like retrieving information, processing documentation, and handling text-based queries - are exactly what generative AI excels at. AI-powered chatbots and voice systems are already managing routine customer inquiries, processing returns, and resolving common issues.
This shift is not just theoretical; it’s happening now. In 2025, approximately 76,440 jobs were eliminated in roles like data entry, telemarketing, and administrative support due to AI-driven automation. Call centers and bookkeeping are prime examples of how specific tasks are being redefined.
In industries like finance and healthcare, administrative roles are transitioning to a hybrid model. AI takes over repetitive tasks such as data entry, tax filing, and medical coding, while human workers focus on oversight and managing exceptions. For instance, bookkeepers now rely on AI to reconcile accounts and flag potential errors, freeing them to prioritize strategic financial analysis and client interactions.
However, not all layoffs attributed to AI reflect genuine technological readiness. Some companies are using AI as a pretext for cost-cutting. Forrester analysts call this trend "AI washing", where staff reductions are disguised as advancements in AI adoption. Interestingly, over half of the layoffs blamed on AI in 2026 are expected to be reversed as businesses realize they acted prematurely.
Wage Trends and Job Changes
As automation takes over routine tasks, wages and job roles are also evolving:
| Role Category | Displacement Risk | Augmentation Potential | Wage Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Service | High (Routine tasks) | High (AI-assisted chat/voice) | Entry-level wages decline; advanced AI management roles see higher pay |
| Administrative/Clerical | High (Data entry/scheduling) | Moderate (Workflow automation) | Stagnant wages for routine roles; higher pay for AI-savvy administrators |
| Bookkeeping/Accounting | High (Basic entry/reconciliation) | High (Audit/Strategic analysis) | Growth in wages for advisory and strategic roles |
Entry-level positions in AI-affected jobs have seen a 13% wage drop compared to less-impacted roles. Younger workers, especially those aged 22–25, are particularly vulnerable since many of these jobs previously served as stepping stones for building experience.
But it’s not all bad news. AI is more likely to augment jobs (impacting 20% of roles) than to replace them entirely (6.1% of roles). Companies that embrace AI often experience 6% higher employment growth and 9.5% more sales growth over five years. This indicates that while some roles may disappear, new opportunities emerge for workers who adapt and develop hybrid skills.
Professionals who can oversee AI systems, interpret outputs, and handle complex exceptions are now commanding higher salaries. On the flip side, those stuck in purely routine tasks face stagnant or declining wages. The unemployment rate among college graduates hit 5.8% in March 2025 - the highest in over four years - partly due to AI displacing workers without these hybrid skills.
"An increasingly pertinent debate centers on AI's impact on employment, especially as more companies are reportedly deploying AI models to augment or displace existing workers, particularly with roles that involve routine and repetitive tasks such as data entry and customer service." – Brenda Duverce, Senior Analyst, J.P. Morgan
For workers in these high-risk sectors, the takeaway is clear: focus on transitioning from routine tasks to roles that involve directing and validating AI outputs. By combining human expertise with AI oversight, employees can position themselves for success in this rapidly changing landscape.
sbb-itb-20a3bee
Healthcare and Skilled Trades: Lower Disruption Risk
AI's impact isn't uniform across industries. While automation has significantly transformed areas like customer service and administrative roles, sectors like healthcare and skilled trades remain more stable. These fields leverage AI as a supportive tool, relying heavily on human skills that technology can't replicate.
AI Supporting Healthcare Roles
Healthcare is experiencing rapid advancements in AI, but the focus is on enhancing human expertise, not replacing it. By 2030, the global healthcare sector is expected to face a shortage of 18 million professionals, including 5 million doctors. Meanwhile, demand for healthcare workers is projected to grow between 23% and 30% from 2022 to 2030, requiring an additional 3.5 million health aides, technicians, and wellness workers.
AI is already making strides in improving diagnostics and treatment. For example, Microsoft Research's InnerEye technology, introduced in 2021, automates tumor contouring for radiotherapy, cutting manual preparation time by up to 90%. Another breakthrough, the FDA-approved IDx-DR system, autonomously detects diabetic retinopathy with impressive accuracy - 87% sensitivity and 90% specificity - allowing primary care providers to perform screenings without needing an ophthalmologist.
These tools don't replace healthcare professionals but instead act as powerful aids. AI processes vast datasets, turning patterns into actionable insights for doctors. However, it lacks critical human qualities like common sense, clinical intuition, and empathy. Skills like interpersonal communication and relationship-building remain irreplaceable components of healthcare.
"AI is perhaps the most transformational technology of our time, and healthcare is perhaps AI's most pressing application." – Satya Nadella, CEO, Microsoft
AI also plays a role in reducing administrative burdens. For instance, it streamlines nursing documentation, allowing nurses to spend more time with patients. This underscores the importance of the "human-in-the-loop" model, where AI handles data, and humans provide ethical and contextual judgment.
"Data show that nursing's person-centeredness protects against job displacement by AI." – Nursing Outlook
While healthcare thrives on AI's ability to augment human capabilities, skilled trades offer a different kind of stability.
Stability in Skilled Trades
Jobs in skilled trades - like HVAC technicians, electricians, and construction workers - are among the least affected by AI. These roles require physical dexterity, situational awareness, and adaptability, which current technology struggles to replicate.
Although AI could theoretically take on tasks accounting for 44% of U.S. work hours, robots are only capable of automating 13% of hours involving physical work. Skilled trades often involve non-routine tasks in unpredictable environments, making them resistant to automation.
For example, the construction industry faced a shortage of 400,000 workers in early 2023. With federal infrastructure projects driving demand, job growth in this sector is expected to rise by 12% between 2022 and 2030. Physical work is projected to account for nearly 31% of workforce time by 2030.
"Most physical work still demands fine motor skills, dexterity, and situational awareness that technology cannot yet replicate reliably." – McKinsey
High costs and technological limitations also play a role. Humanoid robots, priced between $150,000 and $500,000 per unit with battery lives of just 2–4 hours, aren't practical for large-scale adoption in trades. Meanwhile, job postings reflect growing demand for physical skills, further emphasizing the resilience of these roles.
| Occupational Category | AI Impact Type | Automation Risk | Key Protection Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Professionals | Augmentation | Low | Empathy, clinical intuition, human judgment |
| Skilled Trades | Complementary | Low (13% of hours) | Physical dexterity, unpredictable environments |
The message is clear: AI isn't replacing these professions - it’s a tool to complement human expertise. Whether it's a nurse’s compassion or an electrician's hands-on problem-solving, these fields demonstrate the enduring value of human skills. Learning to work alongside AI will be essential for staying competitive in the evolving job market.
"Work in the future will be a partnership between people, agents, and robots - all powered by AI." – McKinsey
These examples underscore the importance of human expertise in healthcare and skilled trades, showing how these sectors can adapt and thrive alongside technological advancements.
Cross-Industry Trends and How to Prepare
AI is transforming industries and reshaping how work gets done, pushing millions to adapt their skills to stay relevant. It's important to note that AI is driving job transformation, not elimination. Instead of replacing entire roles, AI automates specific tasks, freeing up workers to focus on complex problem-solving, creativity, and decision-making. For instance, companies that heavily integrate AI report 6% higher employment growth and 9.5% greater sales growth over five years. As Lareina Yee, Senior Partner at McKinsey & Company, explains:
"Work in the future will be a partnership between people, agents, and robots - all powered by AI."
Interestingly, over 70% of the skills employers value remain relevant, even as automation grows. The challenge lies in adapting these skills to work seamlessly with AI, creating both hurdles and opportunities for workers across all industries.
Upskilling and Retraining for AI-Era Jobs
One of the fastest-rising demands across industries is AI fluency - the ability to effectively use and manage AI tools. This demand has skyrocketed, growing 7x in just two years. AI fluency involves more than just knowing how to operate tools; it’s about asking the right questions, interpreting AI outputs, and validating results.
To thrive in this environment, workers need a balanced skill set that combines technical know-how with enduring human abilities. While AI excels at data processing, it cannot replicate human traits like empathy, leadership, and emotional intelligence. Skills such as negotiation, coaching, and team management are still highly sought after. In fact, jobs requiring at least one new digital or technical skill offer a 3% salary premium, while positions demanding four or more such skills can pay up to 8.5% more in the U.S..
"AI will not make most human skills obsolete, but it will change how they are used." – McKinsey Global Institute
You don’t need to wait for formal training programs to get started. Begin exploring AI tools today to enhance your skills and optimize your workflow. Workers who succeed in this shift are those who identify repetitive tasks for automation and redirect their efforts toward strategic thinking and decision-making.
Employers are also moving away from traditional credential-based hiring, focusing instead on skills-based evaluations. This shift places greater emphasis on practical experience and adaptability over four-year degrees. Demonstrating hands-on capabilities with emerging technologies can open doors, even without formal certifications. As skill demands evolve, preparing for interviews becomes a key opportunity to showcase your AI proficiency.
Using Acedit for Career Success
In this changing landscape, having the right tools can make all the difference. One such tool is Acedit (https://acedit.ai), an AI-powered Chrome extension designed to help job seekers stand out.
Acedit offers real-time interview coaching and personalized preparation tools. Its features include real-time question detection, AI-generated response suggestions, and interview simulations. These tools help you articulate your experience with AI and demonstrate your ability to adapt to technological advancements. Additionally, Acedit’s Q&A generator customizes practice questions based on specific job descriptions and industry needs, ensuring you’re ready to tackle the challenges of today’s job market.
Beyond interviews, Acedit also supports users with AI-driven cover letter creation and LinkedIn profile optimization. These features ensure your application materials highlight your readiness for the AI-driven workplace. With options ranging from a free tier to lifetime access plans, Acedit is a resource for everyone - from those transitioning careers to professionals stepping into roles where humans and AI collaborate to produce results.
Conclusion
AI is transforming the workplace, not by eliminating jobs but by reshaping how work gets done. By 2030, up to 30% of hours worked could be automated. However, companies that embrace AI extensively report 6% higher employment growth and 9.5% greater sales growth over five years, proving that AI can fuel productivity and expansion rather than job loss. The real challenge lies in how workers respond - those who evolve their skills and collaborate with AI will thrive, while resistance to change may lead to setbacks.
This shift highlights the urgency for action. Success in this evolving job market requires a balanced approach to skill development. Mastering AI tools while refining human abilities like critical thinking and emotional intelligence is crucial. Currently, 1 in 10 job postings in advanced economies demands at least one new skill, and these roles offer a 3% to 15% pay premium. Moreover, workers in lower-wage positions are up to 14 times more likely to need occupational transitions than those in higher-wage roles, making proactive upskilling a necessity.
As Lawrence D. W. Schmidt from MIT Sloan explains:
"Firms that adopt AI don't necessarily need to shed workers; they can grow and make more stuff and use workers more efficiently than other firms".
This productivity-driven growth opens doors for those ready to adapt and seize new opportunities.
Looking ahead, with 12 million occupational transitions projected by 2030, taking steps now is essential. Tools like Acedit (https://acedit.ai) can provide AI-powered interview coaching and personalized preparation to help workers navigate career changes or advance in their current roles. Demonstrating adaptability and readiness for AI-driven work will set successful candidates apart.
As emphasized earlier, treating AI as a partner rather than a threat is the key to success. Those who embrace AI as a tool to enhance their abilities will find themselves better positioned to thrive in the future of work. Start building that partnership today.
FAQs
How can workers adapt to AI-driven changes in their industries?
To succeed in industries transformed by AI, workers should focus on building skills that complement automation rather than compete with it. While AI efficiently handles tasks like data entry, human strengths such as critical thinking, creative problem-solving, and emotional intelligence continue to be irreplaceable. Developing expertise in interpreting AI-generated insights, guiding strategic decisions, and managing AI tools can make a big difference in staying relevant.
Ongoing learning is crucial. Enhancing skills in areas like STEM, digital literacy, and management can help workers maintain a competitive edge. Platforms like Acedit, an AI-driven tool, offer real-time interview coaching and personalized preparation, helping job seekers meet the demands of a rapidly changing job market. Embracing lifelong learning and staying flexible are essential strategies for navigating the evolving world of work shaped by AI advancements.
Which industries are least impacted by AI automation?
Industries that remain mostly untouched by AI automation are those that depend heavily on human-centric skills like emotional intelligence, creativity, and quick decision-making. Take healthcare as an example - this field often involves intricate interpersonal interactions and physical tasks that AI struggles to replicate effectively. Similarly, jobs in education, legal services, and creative professions rely on human judgment and adaptability, making them less susceptible to replacement by machines.
Jobs requiring a physical presence or hands-on work, such as specific service roles, also tend to be more resistant to AI disruptions. While automation excels at handling repetitive or routine tasks, positions that thrive on human connection, problem-solving, and originality continue to play a vital role in today’s job market.
What new job roles are emerging in the tech industry due to advancements in AI?
AI is reshaping the job market, bringing a wave of fresh opportunities in the tech industry. Roles like Decision Designer and AI Experience Officer are gaining traction as businesses prioritize refining AI-driven decisions and enhancing how users interact with AI systems.
Other noteworthy positions include Knowledge Architect, Orchestration Engineer, Conversation Designer, and Human-AI Collaboration Leader. These roles focus on seamlessly weaving AI into everyday business operations. The boom in generative AI has also led to roles like Prompt Engineer and AI Systems Architect, which specialize in fine-tuning AI prompts and crafting intricate AI frameworks. Together, these emerging careers underscore the growing demand for professionals skilled in navigating this rapidly evolving field.